LT1366(Rev_A) 查看數據表(PDF) - Linear Technology
零件编号
产品描述 (功能)
生产厂家
LT1366 Datasheet PDF : 20 Pages
| |||
LT1366/LT1367
LT1368/LT1369
TYPICAL APPLICATIONS
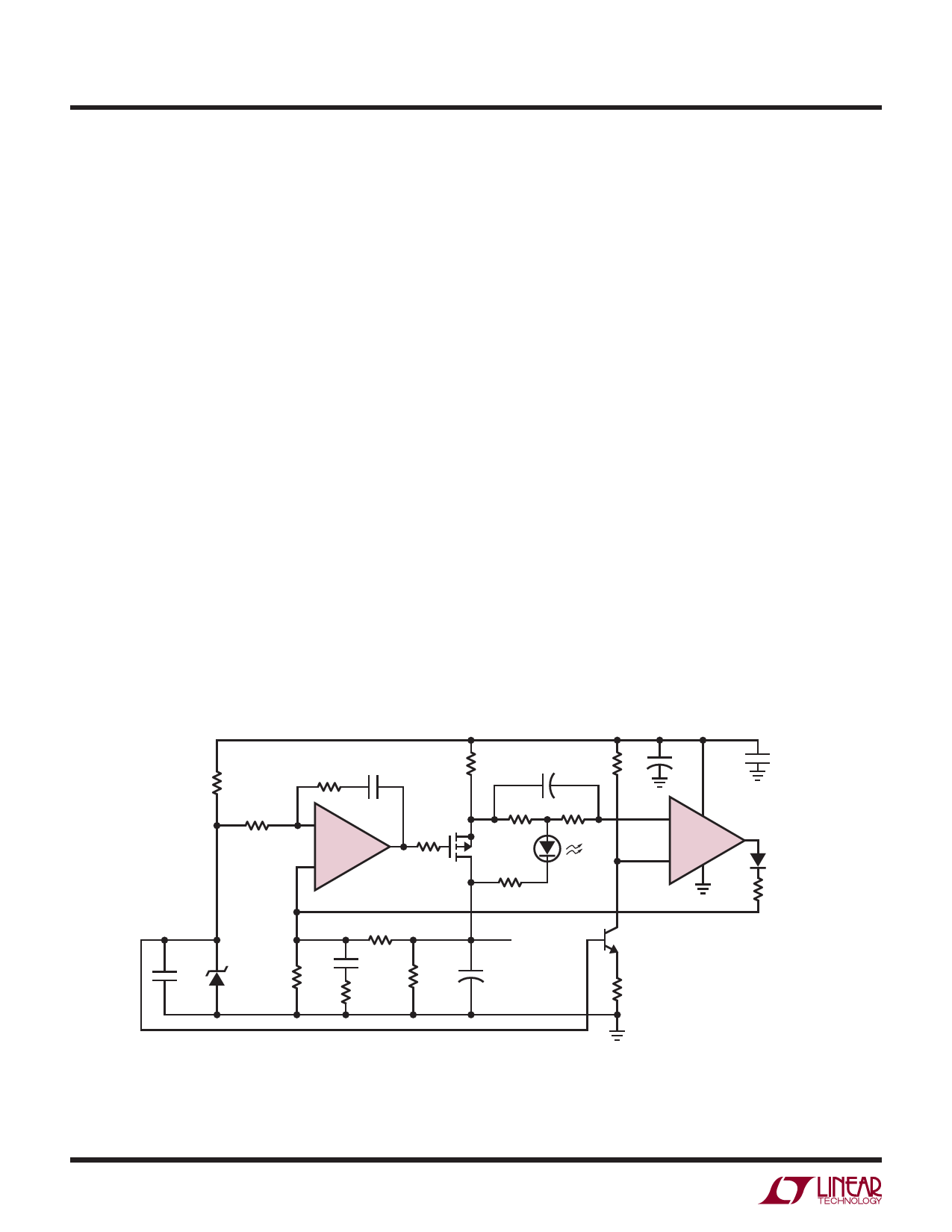
Precision Low Dropout Regulator
Microprocessors and complex digital circuits frequently
specify tight control of power supply characteristics. The
circuit shown in Figure 6 provides a precise 3.6V, 1A
output from a minimum 3.8V input voltage. The circuit's
nominal operating voltage is 4.75V ±5%. The voltage
reference and resistor ratios determine output voltage
accuracy, while the LT1366’s high gain enforces 0.2% line
and load regulation. Quiescent current is about 1mA and
does not change appreciably with supply or load. All
components are available in surface mount packages.
The regulator’s main loop consists of A1 and a logic level
FET, Q1. The output is fed back to the op amp’s positive
input because of the phase inversion through Q1. The
regulator’s frequency response is limited by Q1’s roll-off
and the phase lead introduced by the output capacitor’s
effective series resistance (ESR). Two pole-zero networks
compensate for these effects. The pole formed with R5
and C2 rolls off the gain set with the feedback network,
while the pole formed with R7 and C3 rolls off A1’s gain
directly, which is the dominant influence on settling time.
The zeros formed with R6 and C2, and R8 and C3 provide
phase boost near the unity-gain crossover, which in-
creases the regulator’s phase margin. Although not di-
rectly part of the compensation, R9 decouples the op
amp’s output from Q1’s large gate capacitance.
A second loop provides a foldback current limit. A2
compares the sense voltage across R1 with 50mV refer-
enced to the positive rail. When the sense voltage exceeds
the reference, A2’s output drives Q1’s gate positive via A1.
In current limit, the output voltage collapses and the
current limit LED (D1) turns on causing about 30mV to
drop across R3. A2 regulates Q1’s drain current so that the
deficit between the 50mV reference and the voltage across
R3 is made up across the sense resistor. The reduced
sense voltage is 20mV, which sets the current limit to
about 400mA. As the supply voltage increases, the voltage
across R3 increases, and the current limit folds back to a
lower level. The current limit loop deactivates when the
load current drops below the regulated output current.
When the supply turns on rapidly, C1 bypasses the fold
back circuit allowing the regulator to start-up into a heavy
load.
Q1 does not require a heat sink. When mounted on a type
FR4 PC board, Q1 has a thermal resistance of 50°C/W. At
1.4W worst case dissipation, Q1 can operate up to 80°C.
10k
R7
13k
C3
R8
6.8nF
2k
–
A1
1/2 LT1366
+
VIN = 4.75V ±5%
R9
100Ω
R1
0.05Ω
C1
10µF
+
50mV
–
R3 + R4
20Ω
10k
Q1
D1
Si9433DY
1.5k
+
R2
2k
C5
47µF
–
A2
1/2 LT1366
+
0.1µF
D2
1N4148
5k
38.5k*
VOUT = 3.6V
AT 1A
C2
C4
1µF
LT1004-1.2
R5*
20k
6.8nF
R6
+
RMIN**
1k
CLOAD
10µF
6.2k
Q2
2N3904
23.2k
*1% METAL FILM
4.75V TO 3.6V LDO AT 1A
**SET RMIN BASED ON LOAD CHARACTERISTICS
LT1366 F06
Figure 6. Precision 3.6V, 1A Low Dropout Regulator
14