STMicroelectronics
AN4021 Hoja de datos - STMicroelectronics
Introduction
This application note explains how to calculate reverse losses in a power diode by taking into account the impact of the junction temperature (Tj) as well as the reverse voltage VR on the leakage current.
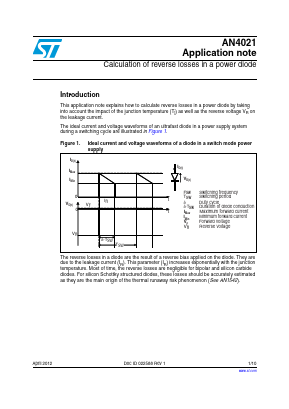
The ideal current and voltage waveforms of an ultrafast diode in a power supply system during a switching cycle are illustrated in Figure 1.
The reverse losses in a diode are the result of a reverse bias applied on the diode. They are due to the leakage current (IR). This parameter (IR) increases exponentially with the junction temperature. Most of time, the reverse losses are negligible for bipolar and silicon carbide diodes. For silicon Schottky structured diodes, these losses should be accurately estimated as they are the main origin of the thermal runaway risk phenomenon (See AN1542).