87LPC762 View Datasheet(PDF) - NXP Semiconductors.
Part Name
Description
MFG CO.
87LPC762
NXP Semiconductors.
87LPC762 Datasheet PDF : 58 Pages
| |||
Philips Semiconductors
Low power, low price, low pin count (20 pin)
microcontroller with 2 kbyte OTP
Preliminary data
87LPC762
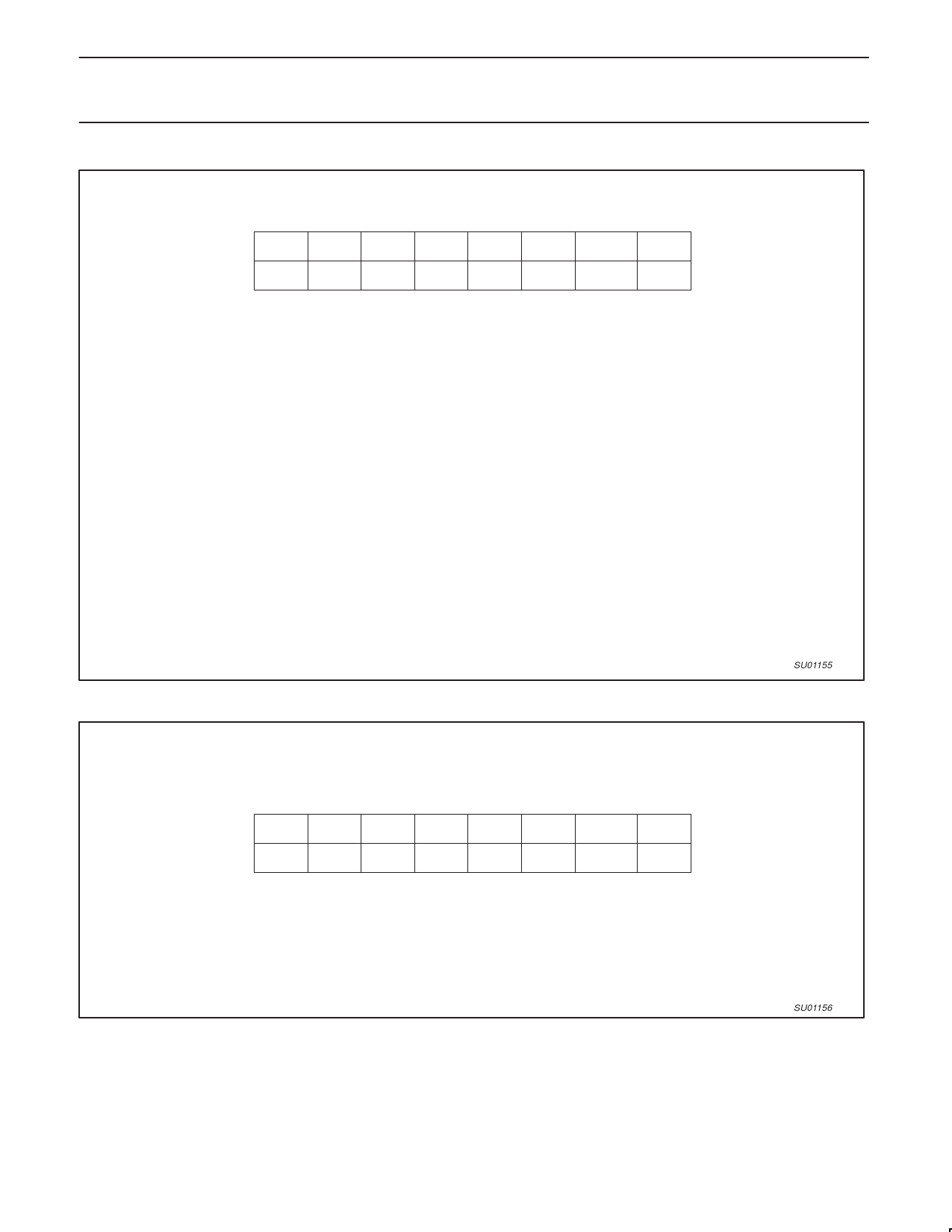
I2CON
Address: D8h
Bit Addressable1
7
READ RDAT
WRITE CXA
6
ATN
IDLE
5
4
DRDY ARL
3
STR
2
1
0
STP MASTER —
CDR CARL CSTR CSTP XSTR XSTP
Reset Value: 81h
BIT
I2CON.7
“
I2CON.6
“
I2CON.5
“
I2CON.4
“
I2CON.3
“
I2CON.2
“
I2CON.1
“
I2CON.0
“
SYMBOL
RDAT
CXA
ATN
IDLE
DRDY
CDR
ARL
CARL
STR
CSTR
STP
CSTP
MASTER
XSTR
—
XSTP
FUNCTION
Read: the most recently received data bit.
Write: clears the transmit active flag.
Read: ATN = 1 if any of the flags DRDY, ARL, STR, or STP = 1.
Write: in the I2C slave mode, writing a 1 to this bit causes the I2C hardware to ignore the bus until it
is needed again.
Read: Data Ready flag, set when there is a rising edge on SCL.
Write: writing a 1 to this bit clears the DRDY flag.
Read: Arbitration Loss flag, set when arbitration is lost while in the transmit mode.
Write: writing a 1 to this bit clears the CARL flag.
Read: Start flag, set when a start condition is detected at a master or non-idle slave.
Write: writing a 1 to this bit clears the STR flag.
Read: Stop flag, set when a stop condition is detected at a master or non-idle slave.
Write: writing a 1 to this bit clears the STP flag.
Read: indicates whether this device is currently as bus master.
Write: writing a 1 to this bit causes a repeated start condition to be generated.
Read: undefined.
Write: writing a 1 to this bit causes a stop condition to be generated.
SU01155
Figure 6. I2C Control Register (I2CON)
I2DAT
Address: D9h
Not Bit Addressable
Reset Value: xxh
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
READ RDAT —
—
—
—
—
—
—
WRITE XDAT —
—
—
—
—
—
—
BIT
I2DAT.7
SYMBOL
RDAT
“
XDAT
I2DAT.6–0
–
FUNCTION
Read: the most recently received data bit, captured from SDA at every rising edge of SCL. Reading
I2DAT also clears DRDY and the Transmit Active state.
Write: sets the data for the next transmitted bit. Writing I2DAT also clears DRDY and sets the
Transmit Active state.
Unused.
SU01156
Figure 7. I2C Data Register (I2DAT)
Checking ATN and DRDY
When a program detects ATN = 1, it should next check DRDY. If
DRDY = 1, then if it receives the last bit, it should capture the data
from RDAT (in I2DAT or I2CON). Next, if the next bit is to be sent, it
should be written to I2DAT. One way or another, it should clear
DRDY and then return to monitoring ATN. Note that if any of ARL,
STR, or STP is set, clearing DRDY will not release SCL to high, so
that the I2C will not go on to the next bit. If a program detects
ATN = 1, and DRDY = 0, it should go on to examine ARL, STR,
and STP.
2001 Oct 26
13