BD3021HFP-M(2009) View Datasheet(PDF) - ROHM Semiconductor
Part Name
Description
View to exact match
BD3021HFP-M Datasheet PDF : 5 Pages
| |||
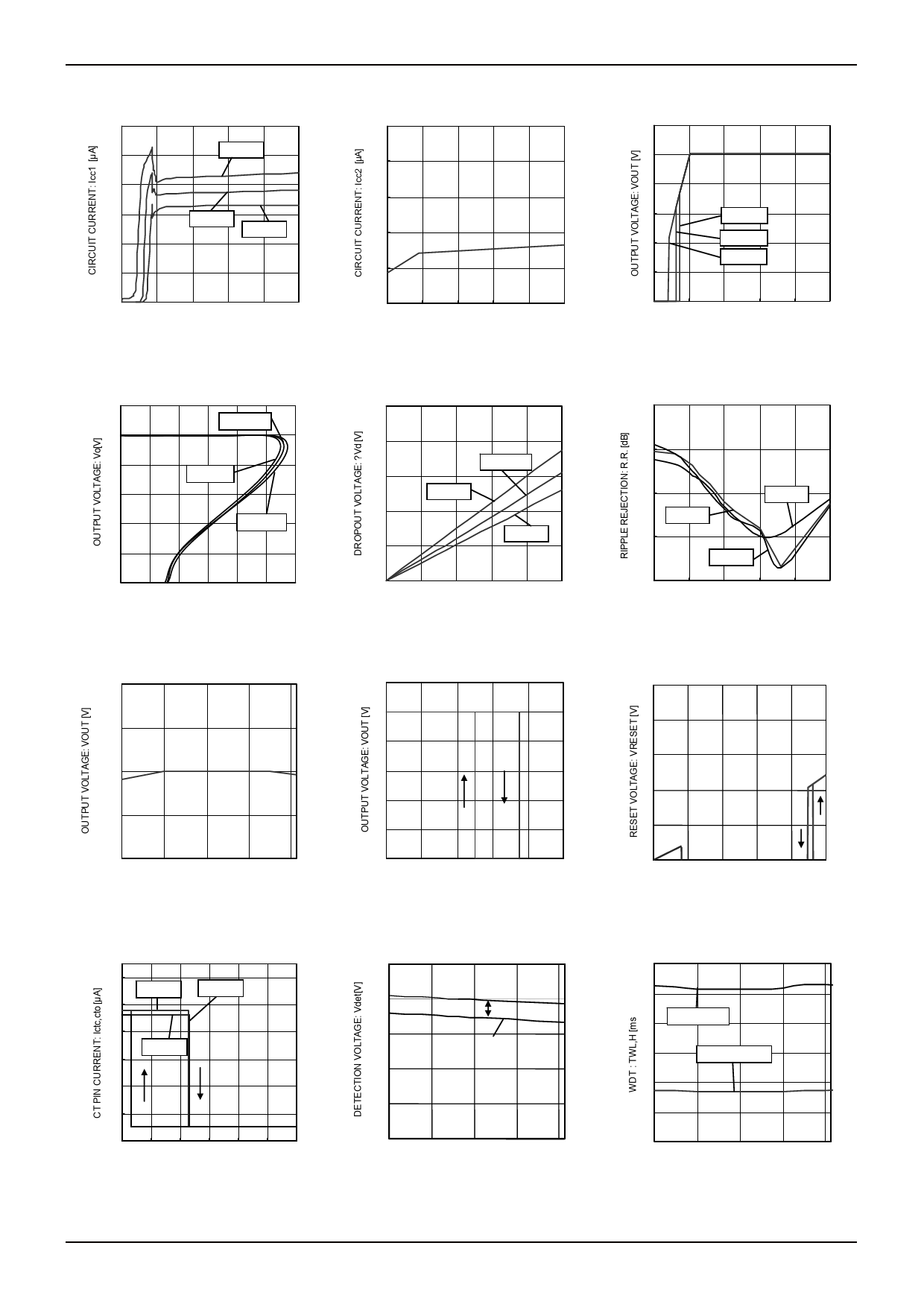
○BLOCK DIAGRAM
Vcc
TSD
VREF
PREREG
3/4
○Pin Number, Pin Name
OCP
edge
Vcc
ON/OFF
Curcuit
VREF_R
Pin
Number
CLK
1
2
INH
3
Vcc
4
5
GND
6
VOUT
7
FIN
RESET
Pin
Name
CLK
INH
Vcc
GND
VOUT
RESET
CT
GND
Function
Clock Input from
Microcontroller
WDT ON/OFF Function Pin
Power Supply Pin
GND
Voltage Output Pin
Reset Output Pin
External Capacitance for Reset
Output Delay Time, WDT Monitor
Time Setting Connection Pin
GND
WDT
CT
VREF_R
VthL
VthH
○Pin Settings / Precautions
1. Vcc pin
Insert a 0.33μF~1000μF capacitor between the Vcc and GND pins.The appropriate capacitance value varies by application. Be sure to
allow a sufficient margin for input voltage levels.
2. Output pins
It is necessary to place capacitors between each output pin and GND to prevent oscillation on the output. Usable capacitance values range
from 0.1μF~1000μF. Abrupt fluctuations in input voltage and load conditions may affect the output voltage. Output capacitance values
should be determined only through sufficient testing of the actual application.
○Operation Notes
1. Absolute maximum ratings
Use of the IC in excess of absolute maximum ratings (such as the input voltage or operating temperature range) may result in damage to the
IC. Assumptions should not be made regarding the state of the IC (e.g., short mode or open mode) when such damage is suffered. If
operational values are expected to exceed the maximum ratings for the device, consider adding protective circuitry (such as fuses) to
eliminate the risk of damaging the IC.
2. Electrical characteristics described in these specifications may vary, depending on temperature, supply voltage, external circuits and
other conditions. Therefore, be sure to check all relevant factors, including transient characteristics.
3. GND potential
The potential of the GND pin must be the minimum potential in the system in all operating conditions. Ensure that no pins are at a voltage
below the GND at any time, regardless of transient characteristics.
4. Ground wiring pattern
When using both small-signal and large-current GND traces, the two ground traces should be routed separately but connected to a single
ground potential within the application in order to avoid variations in the small-signal ground caused by large currents. Also ensure that the
GND traces of external components do not cause variations on GND voltage. The power supply and ground lines must be as short and thick
as possible to reduce line impedance.
5. Inter-pin shorts and mounting errors
Use caution when orienting and positioning the IC for mounting on printed circuit boards. Improper mounting may result in damage to the IC.
Shorts between output pins or between output pins and the power supply or GND pins (caused by poor soldering or foreign objects) may
result in damage to the IC.
6. Operation in strong electromagnetic fields
Using this product in strong electromagnetic fields may cause IC malfunction. Caution should be exercised in applications where strong
electromagnetic fields may be present.
REV. B